
Introduction
Black pepper’s influence on weight loss is multifaceted. It has been shown to boost metabolism by increasing thermogenesis, the process by which your body burns calories to produce heat. Additionally, black pepper improves digestion by stimulating the secretion of digestive enzymes and increasing the absorption of nutrients, which helps the body efficiently process and use energy. Piperine also plays a role in suppressing the formation of new fat cells and enhancing the body’s ability to burn existing fat. Moreover, it has appetite-suppressing effects and can modulate hormones related to hunger, such as ghrelin and leptin.
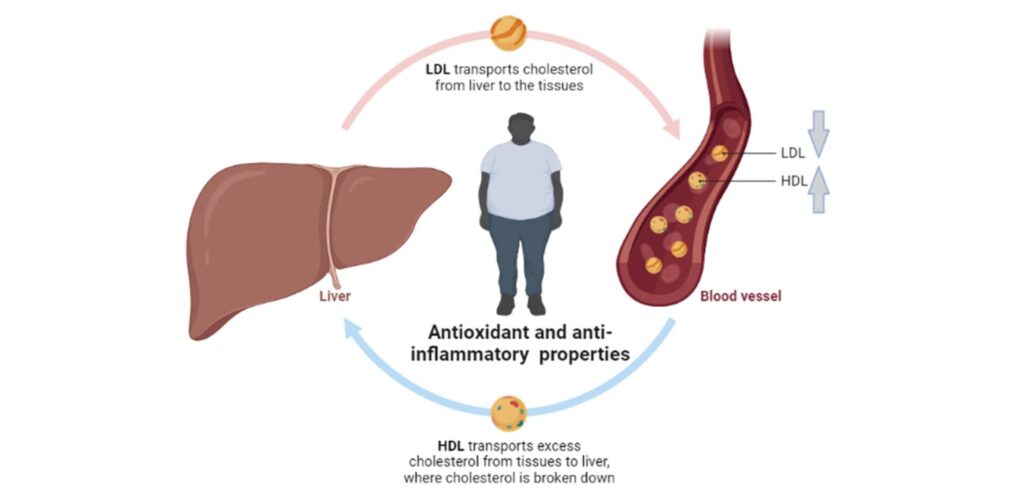
Furthermore, black pepper’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties contribute to overall metabolic health, reducing the risk of obesity-related conditions like insulin resistance. By incorporating black pepper into your diet, either through food or supplementation, you can leverage its natural properties We have good quality pepper shop now to support your weight loss journey. This introduction sets the stage for a deeper exploration of how black pepper can be a powerful ally in achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
1. Metabolic Enhancement and Thermogenesis
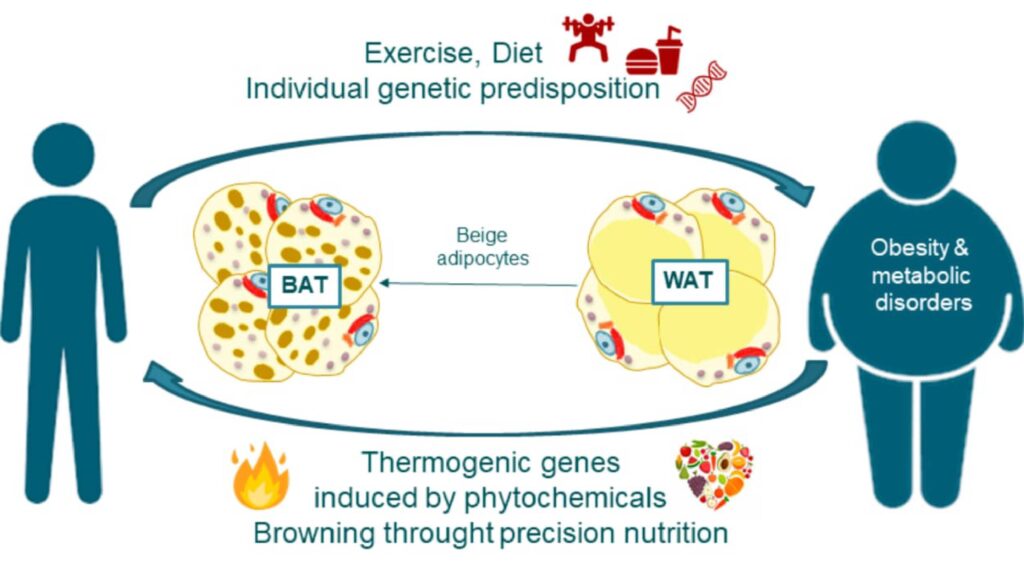
- Detailed Mechanisms of Thermogenesis: Black pepper, through piperine, activates thermogenesis by increasing the secretion of catecholamines, such as adrenaline and noradrenaline, from the adrenal glands. These hormones bind to beta-adrenergic receptors on brown adipose tissue (BAT) and white adipose tissue (WAT). This binding stimulates the breakdown of triglycerides into free fatty acids (FFAs) within adipocytes. These FFAs are then oxidized in the mitochondria to produce heat, a process mediated by uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) in brown fat. The activation of UCP1 uncouples oxidative phosphorylation, meaning the energy from electron transport is released as heat rather than stored as ATP, leading to increased energy expenditure.

- Influence on the Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS): Piperine also activates the sympathetic nervous system, which plays a key role in energy expenditure. The SNS stimulates BAT thermogenesis and lipolysis in WAT through the release of catecholamines. Increased SNS activity boosts overall metabolic rate and enhances fat burning, making black pepper an effective tool in weight management.
- Mitochondrial Biogenesis: Piperine has been found to promote mitochondrial biogenesis—the process by which new mitochondria are formed in cells. This is crucial because mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, responsible for burning calories and producing energy. By increasing the number of mitochondria, piperine enhances the cell’s ability to burn fat and generate energy, contributing to weight loss.
2. Digestive Efficiency and Gastrointestinal Health
- Microbiome Modulation: Piperine has been shown to positively alter the gut microbiome, which is increasingly recognized as a significant factor in weight management. A balanced microbiome aids in efficient digestion, reduces inflammation, and regulates energy harvest from food. Specifically, piperine promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria like Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus while suppressing the growth of pathogenic bacteria. This balanced gut environment can reduce the extraction of excess calories from the diet and lower the risk of weight gain.
- Bile Acid Secretion: Piperine enhances the secretion of bile acids, which are crucial for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats. By improving fat digestion, black pepper ensures that fats are efficiently broken down and absorbed rather than being stored as body fat. Bile acids also act as signaling molecules that regulate lipid metabolism and energy balance, further supporting weight loss.
Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Metabolism: Piperine improves insulin sensitivity by increasing the expression of glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) in muscle cells. GLUT4 is responsible for the uptake of glucose into cells in response to insulin. Enhanced glucose uptake reduces blood sugar levels and minimizes the storage of glucose as fat, which is particularly beneficial for weight loss. Improved insulin sensitivity also means that the body can more effectively use glucose for energy rather than storing it as fat, which can prevent weight gain.
3. Adipogenesis Suppression and Lipid Metabolism
Detailed Pathways in Adipogenesis: Adipogenesis involves the differentiation of preadipocytes into mature adipocytes, a process regulated by several transcription factors, including PPARγ, CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins (C/EBPs), and sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs). Piperine inhibits these transcription factors, particularly PPARγ, which plays a central role in fat cell formation. By downregulating PPARγ, piperine reduces the conversion of preadipocytes into fat-storing adipocytes, limiting the body’s capacity to store excess energy as fat.

- AMP-Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) Pathway: AMPK is a key energy sensor in cells that, when activated, enhances catabolic processes (like fat burning) and inhibits anabolic processes (like fat storage). Piperine activates AMPK, leading to increased fatty acid oxidation and reduced lipogenesis. This shift from fat storage to fat burning is crucial for weight loss. AMPK activation also inhibits the expression of enzymes involved in lipogenesis, such as acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) and fatty acid synthase (FAS), further reducing fat accumulation.
- Role of Adiponectin: Piperine has been shown to increase levels of adiponectin, a hormone secreted by adipose tissue that enhances insulin sensitivity and promotes fat oxidation. Higher adiponectin levels are associated with lower body fat percentage and a reduced risk of obesity-related metabolic disorders.
4. Enhanced Nutrient Bioavailability and Synergistic Effects
- Interaction with Curcumin: Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, has poor bioavailability due to rapid metabolism and elimination from the body. Piperine inhibits the enzymes responsible for curcumin’s metabolism, allowing more curcumin to remain active in the body for longer periods. This interaction is particularly beneficial in weight loss, as curcumin has anti-inflammatory and fat-burning properties. Together, piperine and curcumin can enhance fat metabolism, reduce inflammation, and support overall metabolic health.
- Impact on Fat-Soluble Vitamins: Piperine increases the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) by enhancing their transport across the intestinal barrier. These vitamins play essential roles in energy metabolism, immune function, and cellular health. For instance, vitamin D is involved in the regulation of calcium and phosphate metabolism, which is crucial for bone health and muscle function. Adequate vitamin D levels are associated with improved insulin sensitivity and reduced risk of obesity.
- Synergy with Other Phytochemicals: Piperine can enhance the bioavailability of various other phytochemicals and antioxidants found in food, such as resveratrol, quercetin, and catechins. These compounds have been shown to support weight loss by promoting fat oxidation, reducing oxidative stress, and improving metabolic health. The combined effects of piperine and these phytochemicals can create a powerful synergy that enhances weight loss outcomes.
5. Appetite Regulation and Hormonal Influence
- Detailed Appetite Control Mechanisms: Piperine influences several appetite-regulating hormones, including GLP-1, CCK, and ghrelin. GLP-1 is released in response to food intake and promotes satiety by slowing gastric emptying and enhancing insulin secretion. Piperine increases GLP-1 levels, helping you feel fuller for longer and reducing overall calorie intake. Similarly, CCK is released by the intestines in response to fat and protein digestion and acts on the brain to signal fullness. Piperine enhances CCK release, contributing to better appetite control.
- Ghrelin Suppression: Ghrelin is a hormone produced in the stomach that stimulates appetite. High ghrelin levels lead to increased hunger and food intake, making it difficult to maintain a calorie deficit for weight loss. Piperine has been shown to lower ghrelin levels, reducing hunger and helping to control calorie intake.
- Impact on Leptin: Leptin is a hormone produced by fat cells that signals to the brain when you have enough energy stored as fat. In obesity, leptin signaling can become impaired, leading to leptin resistance where the brain doesn’t recognize the signals and continues to drive hunger. Piperine may improve leptin sensitivity, helping to regulate appetite and prevent overeating.
6. Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Actions
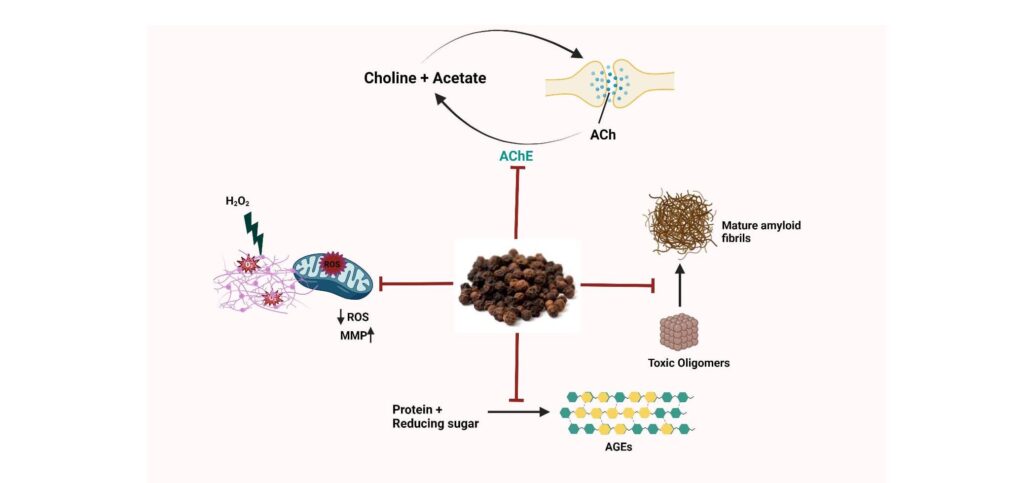
Oxidative Stress and Fat Accumulation: Oxidative stress results from an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body. High levels of oxidative stress can lead to chronic inflammation, which is linked to insulin resistance, fat accumulation, and obesity. Piperine’s potent antioxidant properties help neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and its associated risks. By lowering oxidative stress, piperine supports healthier metabolism and helps prevent the accumulation of excess body fat.

- NF-κB Pathway Inhibition: NF-κB is a key transcription factor that regulates the expression of inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6, which are associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome. Piperine inhibits the activation of the NF-κB pathway, thereby reducing the production of these pro-inflammatory cytokines. This reduction in inflammation can improve insulin sensitivity, reduce fat storage, and support overall metabolic health.
- Role in Adipose Tissue Inflammation: Obesity is often associated with chronic low-grade inflammation in adipose tissue, which contributes to insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction. Piperine reduces the infiltration of immune cells, such as macrophages, into adipose tissue, thereby lowering inflammation. This anti-inflammatory effect can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of obesity-related complications, such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
7. Practical Application and Usage Strategies
- Culinary Incorporation: To maximize the weight loss benefits, use black pepper liberally in your daily cooking. Sprinkle it on salads, soups, eggs, and grilled meats. Pair it with turmeric in curries or golden milk to enhance both flavor and health benefits. Adding black pepper to olive oil-based dressings can also increase the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and antioxidants from vegetables.

- Supplementation Considerations: For those who prefer a more concentrated dose, piperine supplements are available. However, it’s important to use these supplements cautiously, especially if you’re taking other medications, as piperine can affect drug metabolism. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
- Synergy with Exercise: The metabolic and thermogenic effects of piperine are enhanced by physical activity. Regular exercise, combined with a diet rich in black pepper and other thermogenic spices, can significantly boost your weight loss efforts. Consider incorporating black pepper into pre-workout meals to enhance fat oxidation during exercise.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
- Gastrointestinal Issues: While black pepper is generally safe in culinary amounts, excessive consumption can irritate the gastrointestinal tract, leading to symptoms such as heartburn, indigestion, or gastritis. Those with sensitive stomachs or pre-existing gastrointestinal conditions should consume black pepper in moderation.
- Drug Interactions: Piperine’s ability to inhibit cytochrome P450 enzymes can affect the metabolism of certain medications, leading to increased blood levels of these drugs. This can heighten the risk of side effects, particularly with medications like anticoagulants, anticonvulsants, and some antidepressants. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional if you are taking medications and considering increasing your intake of black pepper or piperine supplements.
- Allergic Reactions: Although rare, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to black pepper, including symptoms like rashes, itching, or digestive discomfort. If you notice any adverse reactions after consuming black pepper, discontinue use and seek medical advice.
Conclusion
Black pepper, particularly its active compound piperine, offers a multi-faceted approach to weight loss through mechanisms that enhance metabolism, improve digestion, suppress fat cell formation, increase nutrient absorption, and reduce inflammation. By integrating black pepper into your diet and lifestyle strategically, you can leverage its natural properties to support a healthier weight and overall well-being. Whether used in cooking or as a supplement, black pepper is a potent, natural ally in the journey toward sustainable weight loss.
